Anti-GLN1 GLN2 | GS1 GS2 glutamine synthetase global antibody
(Cat#: AS08 295)
Description
- Immunogen: KLH-conjugated synthetic peptide derived from a wide range of available sequences including all isoforms of Arabidopsis thaliana GLN1-1, 1-2, 1-3 and 1-4, (At5g37600, At1g66200, At3g17820, At5g16570)
- Host: Rabbit
- Clonality: Polyclonal
- Purity: Serum
- Format: Lyophilized
- Quantity: 50 µl
- Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 50 µl of sterile water
- Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube.
- Tested applications: Western blot (WB)
- Recommended dilutions: 1 : 10 000 (WB)
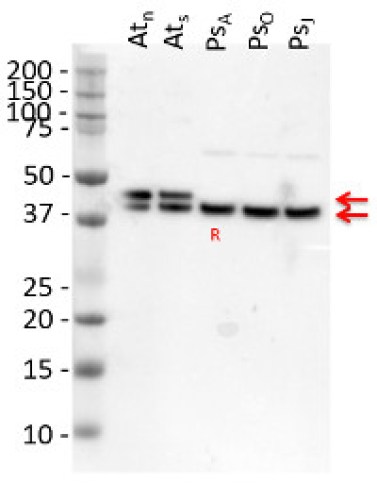
- Expected | apparent MW: 39-40 kDa (GLN1,cytoplasmic form), 44-45 kDa (GLN2, chloroplastic form)
- Confirmed reactivity: Arabidopsis thaliana, Eragrostis tef, Gracilaria gracilis (red algae), Gracilaria lemaneiformis, Leptodictyum riparium (Hedw.) Warnst (moss), Medicago truncatula, Physcomitrium patens, Pinus strobus, Spinacia oleracea, Solanum lycopersicum, Triticum aestivum, Zea mays
- Not reactive in: No confirmed exceptions from predicted reactivity are currently known
- Glutamine synthetase (GLN or GS) is one of the key enzymes involved in nitrogen metabolism of plants. It catalyses the synthesis of glutamine from glutamate and ammonia in an ATP-dependent reaction. There are two general classes of glutamine synthetase in plants: GLN1, a cytosolic form and GLN2, a chloroplastic form. GLN1 is highly abundant in the vascular elements of roots nodules, flowers and fruits, functioning in the assimilation of ammonium and the biosynthesis of glutamine for nitrogen transport. GLN2 is encoded by a single gene and is highly abundant in leaf mesophyll chloroplasts. Here GLN functions in the assimilation of ammonia produced from photorespiration and the reduction of nitrate in the chloroplasts
- Rubio Wilhelmi et al. (2024). Salinity-Induced Photorespiration in Populus Vascular Tissues Facilitate Nitrogen Reallocation. Plant Cell Environ. 2024 Oct 1.doi: 10.1111/pce.15180. Maresca et al. (2021). Biological responses to heavy metal stress in the moss Leptodictyum riparium (Hedw.) Warnst. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 2022 Jan 1;229:113078. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2021.113078. Epub 2021 Dec 17. PMID: 34929502.Silva et al. (2019). Characterization of plant glutamine synthetase S-nitrosation. Nitric Oxide. 2019 Apr 23;88:73-86. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2019.04.006.Wang et al. (2018). Response of Gracilaria lemaneiformis to nitrogen deprivation. Algal Research Volume 34, September 2018, Pages 82-96.Witzel et al. (2017). Temporal impact of the vascular wilt pathogen Verticillium dahliae on tomato root proteome. J Proteomics. 2017 Oct 3;169:215-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2017.04.008.Silva et al. (2015). Possible role of glutamine synthetase of the prokaryotic type (GSI-like) in nitrogen signaling in Medicago truncatula. Volume 240, November 2015, Pages 98–108.Lang et al. (2011).Simultaneous isolation of pure and intact chloroplasts and mitochondria from moss as the basis for sub-cellular proteomics. Plant Cell Rep. 2011 Feb;30(2):205-15.doi: 10.1007/s00299-010-0935-4.
Boca Scientific is your premiere source for high-quality, innovative solutions for Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, Immunology, genetics and other lab products and reagents. We bring leading-edge products from our own-line and around the world to laboratories in the US and Canada. Our goal is to offer excellent solutions to drive research and discoveries backed by superior customer support.
