
FluoMag Red Fluorescent Magnetofection Reagent, 100µl
FluoMag-S for SilenceMag (Cat# FS10100)
Description
FluoMag Transfection Reagents are fluorescently-labeled magnetic nanoparticles for Magnetofection applications. They are as efficient as their non-labeled counterparts and allow the visualization of the nanoparticles in vitro during an experiment. FluoMag must be used with a magnetic plate.
Each FluoMag reagent corresponds to a different magnetofection reagent:
- FluoMag-C - corresponds to CombiMag (transfection reagent enhancer)
- FluoMag-N - corresponds to NeuroMag (neuron transfection)
- FluoMag-P - corresponds to PolyMag (DNA transfection reagent)
- FluoMag-S - corresponds to SilenceMag (siRNA delivery)
- FluoMag-V - corresponds to ViroMag (viral transduction)

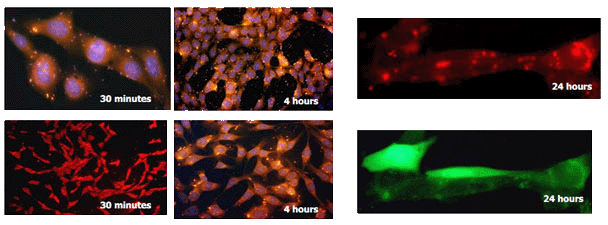
Figure 1: NIH-3T3 transfection with FluoMag-P and pEGFP plasmid DNA. NIH-3T3 cells (5x104 cells/well), growing on coverslips, were transfected in 24-well plates with 1 µg of pEGFP plasmid and 1µL of FluoMag-P per well as described in the Magnetofection instruction manual. At several times post-transfection, cells were fixed, stained with DAPI to detect nucleus (blue) and observed under a fluorescent microscope equipped with a CCD camera.

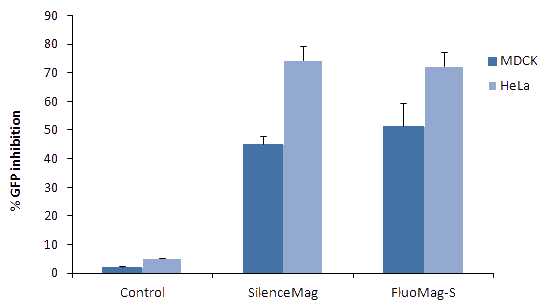
Figure 2: Transfection efficiency of FluoMag-S versus SilenceMag. GFP stably transfected MDCK and HeLa cells were plated the day before transfection in a 24-well plate. Cells were then treated with SilenceMag or FluoMag-S and siRNA (targeting GFP or targeting LacZ as control) as described in the SilenceMag instruction manual. Complexes were prepared with 1 µL of SilenceMag or FluoMag-S and 10nM (67.5ng) of siRNA. Cells were then transfected in 500 µL transfection volume. GFP expression level was monitored 72h post-transfection by detection of fluorescence intensity with a fluorometer.
- Easy cell labeling and tracking
- Non-toxic
- Compatible with serum
- Double labeling and co-localization studies using GFP or FITC labeled nucleic acids
- Transfection mechanisms
- Fluorescent resonance energy transfer (FRET) assay
- Analysis of association of vectors with magnetic nanoparticles
- FC10100 - FluoMag-C Fluorescent Magnetofection Reagent, corresponds to CombiMag, 100µl
- FN10100 - FluoMag-N Fluorescent Magnetofection Reagent, corresponds to NeuroMag, 100µl
- FP10100 - FluoMag-P Fluorescent Magnetofection Reagent, corresponds to PolyMag, 100µl
- FS10100 - FluoMag-S Fluorescent Magnetofection Reagent, corresponds to SilenceMag, 100µl
- FV10100 - FluoMag-V Fluorescent Magnetofection Reagent, corresponds to ViroMag, 100µl
Boca Scientific is your premiere source for high-quality, innovative solutions for Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, Immunology, genetics and other lab products and reagents. We bring leading-edge products from our own-line and around the world to laboratories in the US and Canada. Our goal is to offer excellent solutions to drive research and discoveries backed by superior customer support.

 CombiMag Transfection Enhancing Reagent
CombiMag Transfection Enhancing Reagent NeuroMag Transfection Reagent
NeuroMag Transfection Reagent ViroMag Viral Gene Delivery Reagent
ViroMag Viral Gene Delivery Reagent SilenceMag siRNA Delivery Reagent
SilenceMag siRNA Delivery Reagent