Anti-RFA | Baker's yeast replication factor A
(Cat#: AS07 214)

Description
- Immunogen: RPA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae consisting of three subunits RFA1 (70 kDa), RFA2 (30 kDa) and RFA3 (14 kDa); overexpressed in E.coli and purified by chromatography; no affinity tags were added to any of three subunits
- Host: Rabbit
- Clonality: Polyclonal
- Purity: Serum
- Format: Lyophilized
- Quantity: 50 µl
- Reconstitution: For reconstitution add 50 µl of sterile water
- Storage: Store lyophilized/reconstituted at -20°C; once reconstituted make aliquots to avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. Please remember to spin the tubes briefly prior to opening them to avoid any losses that might occur from material adhering to the cap or sides of the tube.
- Tested applications: Immunoprecipitation (IP), Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP), Western blot (WB)
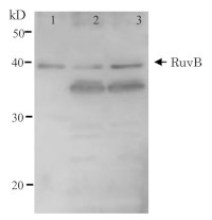
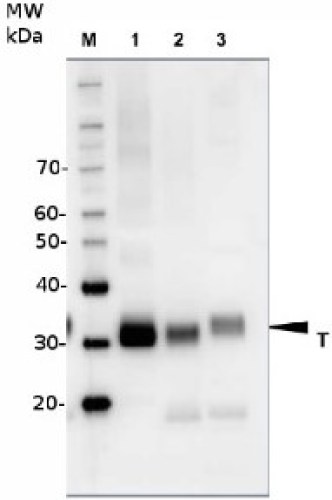
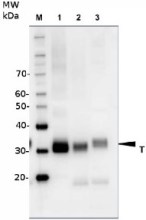
- Expected | apparent MW: ChIP, 1 : 20 000 (WB)
- Confirmed reactivity: 70 + 30 + 14 kDa
- Not reactive in: Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Saccharomyces cerevisiaereplication protein A (RPA), also known as replication factor A (RFA) is a single-stranded DNA-binding protein that is required for multiple processes in eukaryotic DNA metabolism. Those processes include DNA replication, DNA repair, and recombination. Homologues to RPA have been identified in all eukaryotic organisms examined. RPA is heterotrimeric protein composed of subunits of approximately 70, 30, and 14 kDa. Members of this family bind nonspecifically to single-stranded DNA and interact with and/or modify the activities of multiple proteins. Alternative names: Replication protein A 69 kDa DNA-binding subunit, Single-stranded DNA-binding protein, DNA-binding protein BUF2, replication protein A 36 kDa subunit, DNA-binding protein BUF1 antibody
- Galanti et al. (2024). Dbf4-dependent kinase promotes cell cycle controlled resection of DNA double-strand breaks and repair by homologous recombination. Nat Commun. 2024 Apr 3;15(1):2890. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46951-z. Kotenko and Makovets (2024).The functional significance of the RPA- and PCNA-dependent recruitment of Pif1 to DNA. EMBO Rep. 2024 Mar 13. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00114-9. Joo et al. (2024).RPA interacts with Rad52 to promote meiotic crossover and noncrossover recombination. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Feb 10:gkae083.doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae083. Shi et al. (2023).A R-loop sensing pathway mediates the relocation of transcribed genes to nuclear pore complexes.STAR Protoc. 2023 Sep 20;4(4):102577.doi: 10.1016/j.xpro.2023.102577.Scherzer et al (2022). Recruitment of Scc2/4 to double-strand breaks depends on ?H2A and DNA end resection. Life Sci Alliance. 2022 Jan 27;5(5):e202101244. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202101244. PMID: 35086935; PMCID: PMC8807874.Minchell et al. (2020). Cohesin Causes Replicative DNA Damage by Trapping DNA Topological Stress. Mol Cell . 2020 Mar 29;S1097-2765(20)30161-1. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.03.013. He et. al (2019). KEOPS complex promotes homologous recombination via DNA resection. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Apr 2. pii: gkz228. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz228. Jakobsen et al. (2019). Minimal Resection Takes Place during Break-Induced Replication Repair of Collapsed Replication Forks and Is Controlled by Strand Invasion. Cell Rep. 2019 Jan 22;26(4):836-844.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.12.108. (used AS07 214-100, which is a larger size unit of AS07 214)Deshpande et al. (2017). Structural Basis of Mec1-Ddc2-RPA Assembly and Activation on Single-Stranded DNA at Sites of Damage. Mol Cell. 2017 Oct 19;68(2):431-445.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2017.09.019.
Boca Scientific is your premiere source for high-quality, innovative solutions for Cell Biology, Molecular Biology, Immunology, genetics and other lab products and reagents. We bring leading-edge products from our own-line and around the world to laboratories in the US and Canada. Our goal is to offer excellent solutions to drive research and discoveries backed by superior customer support.